The OmniSEO Guide to Sitemaps
When you’re putting together a website, it’s arguably the main consideration to make sure search engines can find and navigate all of your pages easily. This becomes even more important if you’re adding new content to an already indexed site or competing in a particularly competitive niche. That’s where a sitemap comes in handy.
A sitemap, you guessed it, acts like a map of your site for search engines, making it easier for them to crawl each page and point the right users to the right pages and resources, helping internet users to find what they’re looking for.
While not every website needs one, if increased traffic and leads are a goal, you really should have a sitemap.
In this post we’re going to break down everything you need to know about this, but first, for newcomers to the whole idea:
What is a Sitemap, exactly?
A sitemap is simply a file that sets out your website’s structure. It lists your pages and shows how they’re connected.
Search engines such as Google and Bing use sitemaps to understand your content better – like which pages are most important, or which version of a page you want to be ranked in search results.
You can also create sitemaps aimed at real users, if you think your site could be made easier to navigate by this. These help people find the pages they need, improving their overall experience on your site.
At its core, a sitemap helps you organise your website content. Depending on its type, it might include:
- URLs for each page
- Structure or hierarchy of the site’s pages
- Last updated date for each URL
- How frequently each page changes (like weekly or monthly)
- Language for each page, if applicable
- Entries for images and videos
- Entries for news or timely content
Why Sitemaps Matter for SEO

It’s true that search engines don’t need sitemaps to find your content – they can crawl through internal links to discover pages. But a sitemap can make life much easier for them, especially if some of your content is a few clicks away from the homepage.
Sitemaps can also bring orphan pages (those not linked from anywhere else on your site) to search engines’ attention whereas they may otherwise not have been indexed in the search engine at all.
For your content to show up in search results, it needs to be accessible to crawlers like Googlebot and Bingbot. Sitemaps give you a direct way to highlight your most important pages, leading to better visibility, quicker indexing, and potentially higher traffic.
Sitemaps can also share details like how often a page is updated and what kind of content it holds, helping search engines prioritise what to crawl.
Types of Sitemaps: XML vs HTML
There are two main kinds of sitemap: XML and HTML. Each serves a different purpose, and you can choose to use one or both.
XML Sitemaps
XML sitemaps are mainly for search engines. They help crawlers find and understand your content.
They’re usually stored in the root directory of your website – like https://www.yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml.
You can also hide your sitemap from visitors or competitors by renaming it or moving it to a subfolder.
Types of XML sitemaps:
- Image-focused sitemaps – These highlight important images on your site and help search engines find and index them, which is great for sites that heavily feature visuals.
- Video-specific sitemaps – If your site features videos, these sitemaps provide details like the video’s title, duration, and subject, so search engines can better understand and index them.
- News content sitemaps – Designed for websites with constantly updated news content, these help search engines identify and index your latest articles quickly.
Alternatively, you can add tags for images, videos or news directly into your main sitemap file.
An XML sitemap can’t have more than 50,000 URLs or be bigger than 50 MB. If you’re dealing with lots of images, videos or news articles, creating separate sitemaps for each is usually the best approach.
HTML Sitemaps
HTML sitemaps are designed for people. They’re basically web pages with links to your main sections – think of them as a user-friendly directory. They are far from necessary, but can still be helpful in many cases.
Sitemaps and Accessibility
Accessibility is all about making your website usable for everyone, including people with disabilities.
While it’s not a direct ranking factor for SEO, following these guidelines improves the experience for all visitors.
Creating a Sitemap
The first step is deciding whether to create a sitemap by hand or automate it. If your site is small (under 100 pages), you might create it manually. For bigger sites, automation will save you time.
Manually Creating an XML Sitemap
To build an XML sitemap by hand, list all your URLs in a text editor, including any relevant tags like the last modified date (lastmod). Make sure you follow the Sitemap protocol.
Creating an HTML Sitemap
For an HTML sitemap, list out the key pages and organise them in a clear structure. Then have a developer build the page and add it to your site.
Using Sitemap Tools and Plugins
There are loads of plugins and generators out there to make sitemap creation much easier. For example, WordPress users can turn to plugins like Yoast SEO, RankMath, or Simple Sitemap to generate and update XML sitemaps automatically.
If you’re not on WordPress, check out tools like:
- XML-Sitemaps.com
- Dyno Mapper
- WriteMaps
- Screaming Frog
- Octopus.do
These can handle even large or complex sites, with some offering visual sitemaps for easier editing.
Choosing What to Include in Your Sitemap
For XML sitemaps, include only the URLs you want indexed. Skip anything that’s blocked by robots.txt, password-protected, or admin-only.
For HTML sitemaps, keep it focused on what visitors need – no need to list every outdated or irrelevant page.
Deciding How Many Sitemaps You Need
If your site has more than 50,000 URLs, lots of images or videos, or is news-heavy, consider creating multiple sitemaps. This makes it easier for search engines to crawl everything.
For example, an ecommerce site with thousands of product pages might split its sitemap into separate files for each category.
Best Practices for Sitemap Optimisation
Even with automated sitemap generators, it’s good to check and refine your sitemap regularly:
- Remove tracking parameters and special characters from your URLs to keep them clean
- Only include canonical URLs to avoid duplication
- Avoid listing URLs that are marked with a "noindex" tag
- Use UTF-8 encoding so that your sitemap works correctly with special characters
- Include language-specific tags when applicable
- Use a sitemap index file if you have several sitemaps for one website
- Consider dynamic sitemaps that update in real-time as your content changes
It’s also a good idea to review your sitemap at least once a month, or whenever you make major site changes.
Submitting Your Sitemap
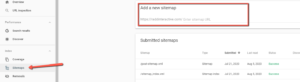
To make sure search engines are using your sitemap, submit it directly. For Google, log in to Google Search Console, select your site, and head to the “Sitemaps” section under “Indexing.” Pop in your sitemap URL and click “Submit.”
You can do the same for Bing, Yahoo, and others using their webmaster tools.
Monitoring Your Sitemap
Keep an eye on how your sitemap is performing. In Google Search Console, you’ll see messages about errors or crawl issues. These can include:
- Invalid dates in your sitemap
- Exceeding the 50,000 URL or 50 MB limit
- Compression problems
- Broken or missing URLs (like 404 errors)
- Unsupported file formats
If you see any errors, take steps to fix them. You can also use tools like Semrush’s Site Audit or Screaming Frog to monitor for issues and get recommendations.
Here are some handy tools for sitemap creation and maintenance:
- Yoast SEO (WordPress plugin, automated sitemap generation)
- PowerMapper (HTML, XML and visual sitemaps)
- Screaming Frog (generate XML sitemaps and find errors)
- Semrush Site Audit (spot sitemap errors and more)
- Slickplan (visual sitemaps for team collaboration)
- Sitebulb (audit sitemap for SEO)
- MonSpark (real-time monitoring)
Choose tools that fit your website’s needs – for example, Slickplan is great for team visualisation, while Yoast SEO is perfect for WordPress sites.
As we’ve hopefully covered, sitemaps aren’t strictly required, but they’re a powerful tool to help search engines and visitors find what they need. A clean, well-maintained sitemap boosts your SEO, speeds up indexing, and improves accessibility for everyone.
So, take the time to set one up and keep it up to date – your website will thank you for it!
On-Page Optimisation in 2025: What’s Changed?
On-page is the backbone of SEO success. It involves tweaking elements on your website to make it more appealing to search engines and users.
In 2025, Google prioritises user experience, content relevance, and technical performance. This guide breaks down the latest key on-page SEO strategies to improve your rankings and drive organic traffic.
But first, for those who are new to this:
What Is On-Page Optimisation?
On-page optimisation means improving elements on your website to rank higher on search engines. The most important elements include content, keywords, meta tags, URLs, and internal links.
Unlike off-page SEO, which focuses on external signals like backlinks, on-page SEO is fully within your control. In 2025, it’s about creating a seamless user experience while aligning with search engine algorithms. Good on-page SEO boosts visibility, click-through rates, and conversions.
Why On-Page SEO Matters in 2025
Search engines are smarter than ever. Google’s algorithms now emphasise user intent, mobile performance, and content quality. On-page optimisation helps your site meet these demands. It ensures your pages load fast, answer user queries, and are easy to navigate.
Studies show that 50% of website traffic comes from organic search, making on-page SEO critical for business growth. Without it, even great content may go unnoticed.
Key On-Page SEO Strategies for 2025
Here are the top techniques to optimise your website, including the most up to date changes. Each focuses on user experience, technical precision, and search intent.
1. Match Search Intent
Search intent is what users want when they type a query. In recent years, Google prioritises content that directly addresses this intent. For example, someone searching “best running shoes” expects a list, not a product page. To optimise, research your target keyword. Check the top-ranking pages to understand user expectations. Create content that delivers exactly what users seek, whether it’s information, a product, or a guide. Tools like Semrush can help identify intent-driven keywords.
2. Optimise Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
Title tags and meta descriptions are your page’s first impression in search results. Keep title tags under 60 characters and include your primary keyword at the start. For example, “Best SEO Tools for 2025” is clear and keyword-rich.
Meta descriptions should be concise, under 120 characters for mobile, and describe the page’s value. Add a call-to-action like “Learn more” to boost clicks. Use tools like Yoast to ensure proper formatting.
3. Use Header Tags Effectively
Header tags (H1, H2, H3) organise your content for users and search engines. Use one H1 tag per page, including your primary keyword. Use H2 and H3 tags to break up content into scannable sections.
This improves readability and helps Google understand your page’s structure. Avoid multiple H1 tags to prevent confusing search bots.
4. Create High-Quality, Intent-Driven Content
It’s probably the biggest cliche in SEO, but content is still king. Write detailed, helpful content that answers user questions.
Aim for at least 1,500 words for in-depth topics, but prioritise quality over length. Include LSI keywords (like “search engine optimisation,” “content marketing,” or “user experience”) naturally to boost relevance.
For example, a post about “SEO strategies” might include terms like “keyword research” or “site speed.” Use tools like Surfer SEO to find content gaps.
5. Improve Site Speed and Core Web Vitals
Site speed is still a top ranking factor, as always. Google’s Core Web Vitals measure loading performance (LCP), interactivity (FID), and visual stability (CLS). Aim for a page load time under 2 seconds.
Compress images using WebP format and enable lazy loading. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights can pinpoint issues. A fast site reduces bounce rates and keeps users engaged.
6. Optimise URLs
Clean URLs help search engines and users understand your page. Include your primary keyword, keep it short, and use hyphens to separate words. For example, “/on-page-seo” is better than “/2025-seo-tips/08/03/2025.” Avoid dates in URLs to keep them evergreen, as well as extraneous details that add extra complexity for no reason. Set up redirects if you change URLs to maintain rankings.
7. Add Internal and Outbound Links
Internal links guide users and search engines through your site. Link to relevant pages using descriptive anchor text. For example, link “SEO checklist” to your SEO guide. Outbound links to high-quality, authoritative sites add credibility. Strategic linking boosts site authority and user experience.
8. Enhance Images and Visuals
Images improve engagement but need optimisation. Use descriptive file names and add alt text with relevant keywords that tell Google what the image is for. Considering compressing images to reduce load time.
Video content is also key. Add explainer videos with transcripts to boost accessibility and rankings.
9. Use Structured Data
Structured data (schema markup) helps search engines understand your content. It enables rich snippets, like star ratings or FAQs, in search results. Use schema for articles, products, or local businesses. Tools like Google’s Rich Results Test ensure proper implementation. This can increase click-through rates by up to 30%.
10. Prioritise Mobile Optimisation
Mobile searches dominate in 2025. Ensure your site is responsive and easy to navigate on small screens. Test forms, buttons, and layouts for mobile usability. Google’s mobile-first indexing means your mobile site is the primary version for rankings. Use tools like Google Search Console to monitor mobile performance.
Tools to Simplify On-Page SEO in 2025
- Semrush: Find keywords, audit sites, and track rankings.
- Google Search Console: Monitor search performance and mobile issues.
- Surfer SEO: Optimise content for relevance and intent.
- Google PageSpeed Insights: Improve site speed and Core Web Vitals.
- Yoast or RankMath: Fine-tune title tags, meta descriptions, and schema.
- Jackdaw Report: Track ranks for key keywords and consistently increase them with OmniSEO.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Keyword Stuffing: Overusing keywords hurts readability and rankings.
- Ignoring Mobile: A non-responsive site loses traffic.
- Neglecting Intent: Content that misses user needs won’t rank.
- Slow Load Times: Pages over 3 seconds drive users away.
- Broken Links: These harm user experience and SEO.
On-page optimisation in 2025 is about balancing technical precision with user-focused content. Focus on search intent, fast load times, and clear navigation. Use tools to streamline your efforts and stay updated on algorithm changes. Start optimising today to boost your rankings and attract more organic traffic. For more tips, feel free to get in touch any time.
What Are Search Terms & Why Do They Matter?
Search terms are the words or phrases people type into search engines like Google or Bing to find information, products, or services online. They’re the foundation of how search engines work, connecting users to the content they’re looking for.
Whether you’re a business owner, a marketer, or just curious about how searches shape the internet, understanding search terms can help you navigate the digital world more effectively. Today we’re breaking down what search terms are, why they matter, and how they’re used to improve online visibility.
What Are Search Terms?

A search term, often called a search query or keyword, is any word or combination of words entered into a search engine. For example, if you type “best coffee shops near me” or “how to bake a cake,” those are search terms. They reflect what a user wants to know, find, or do at that moment.
Search terms can be short, like “pizza delivery,” or longer, like “where to find gluten-free pizza in Cardiff.” They vary widely based on the user’s intent, location, and context. Search engines analyse these terms to deliver the most relevant results, such as websites, images, videos, or maps.
Why Search Terms Matter
Search terms are crucial because they act as a bridge between users and the information they seek. For businesses and website owners, understanding the search terms their audience uses can make or break their online success. Here’s why:
- User Intent: Search terms reveal what users want. Someone searching “buy running shoes” is likely ready to make a purchase, while “how to choose running shoes” suggests they’re researching. Knowing this helps businesses tailor their content or offerings.
- Visibility: Using the right search terms on a website increases the chance of appearing in search results. This is the core of search engine optimisation (SEO).
- Competition: Popular search terms often have high competition. Understanding which terms are worth targeting can help businesses stand out.
- Advertising: In paid search campaigns, like Google Ads, businesses bid on search terms to display their ads. Choosing the right terms ensures ads reach the right audience.
Types of Search Terms
Search terms come in different forms, each serving a unique purpose. Here are the main types:
1. Short-Tail Keywords
These are broad, general terms, usually one or two words, like “dog food” or “car repair.” They attract a large audience but are highly competitive and less specific. For example, “shoes” could mean anything from sneakers to high heels.
2. Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases, like “organic dog food for small breeds” or “affordable car repair in Chicago.” They have lower search volume but are less competitive and often indicate stronger user intent, making them valuable for targeting niche audiences.
3. Informational Queries
These terms are used when someone wants to learn something, like “how to train a puppy” or “what is blockchain.” Websites that provide helpful answers to these queries can build trust and authority.
4. Navigational Queries
These are searches for a specific website or brand, like “YouTube login” or “Amazon deals.” Users already know where they want to go and use the search engine to get there quickly.
5. Transactional Queries
These indicate a desire to take action, such as “buy iPhone 16” or “book a hotel in Paris.” They’re highly valuable for businesses because they often lead to sales or conversions, but they also tend to be highly competitive due to a high percentage of related businesses attempting to rank for them.
6. Local Queries
Local search terms include location-specific words, like “dentist near me” or “best pizza in Seattle.” These are critical for businesses serving specific areas, as they attract nearby customers.
How Search Terms Work in SEO
Search engine optimisation (SEO) is the process of improving a website’s visibility in search results. Search terms play a central role in SEO because they help search engines understand what a website is about. Here’s how they’re used:
- Keyword Research: Tools like Google Keyword Planner or SEMrush help identify popular and relevant search terms. For example, a bakery might find that “gluten-free cupcakes” is a high-value term in their area.
- On-Page SEO: Including search terms in website content, titles, headings, and meta descriptions signals to search engines that the page is relevant to those queries.
- Content Creation: Creating blog posts, guides, or product pages that answer specific search terms attracts organic traffic. For instance, a post titled “How to Choose the Best Laptop for Students” targets an informational query.
- Tracking Performance: Tools like Google Analytics track which search terms drive traffic to a site, helping businesses refine their strategy.
Search Terms and Paid Advertising
In paid search advertising, businesses bid on search terms to show ads to users. For example, a pet store might bid on “dog toys online” to promote their products. The key is choosing terms that balance cost, competition, and relevance. Long-tail keywords are often more cost-effective because they’re less competitive and target users closer to making a purchase.
How to Choose the Right Search Terms
Picking the right search terms requires understanding your audience and goals. Here are some tips:
- Know Your Audience: Think about what your target customers are searching for. Are they looking for information, products, or local services?
- Use Keyword Tools: Tools like Ahrefs, Moz, or Ubersuggest provide data on search volume, competition, and related terms.
- Focus on Intent: Prioritise terms that match the user’s goal, whether it’s learning, navigating, or buying.
- Consider Long-Tail Keywords: These are easier to rank for and often lead to higher conversion rates.
- Analyse Competitors: Look at what terms your competitors rank for to find opportunities.
- Think Local: If you serve a specific area, include location-based terms like “coffee shop in Denver.”
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overusing Keywords: Stuffing a website with too many search terms can make content unreadable and harm SEO.
- Ignoring User Intent: Targeting terms that don’t match what your audience wants can lead to low engagement.
- Focusing Only on Short-Tail Keywords: Broad terms are hard to rank for and may not attract the right audience.
- Neglecting Updates: Search trends change. Regularly review and update your target terms to stay relevant.
The Future of Search Terms
Search technology is evolving. Voice search, for example, has made long-tail, conversational queries like “where can I find a good plumber near me” more common. Artificial intelligence and natural language processing are also making search engines better at understanding context and intent. Staying updated on these trends ensures businesses and individuals can adapt their strategies to remain visible.
Search terms are the heartbeat of online discovery. Whether you’re trying to grow a business, attract readers to a blog, or simply understand how people find information, mastering search terms is key. By focusing on user intent, choosing the right types of keywords, and staying adaptable, you can make the most of search engines to connect with your audience.
LLMs.txt: What is it?
LLMs.txt: What is It?
Imagine you’ve built a fantastic website full of valuable information, but when someone asks an AI like ChatGPT or Claude about your content, it struggles to find or understand it.
In a world where web traffic from search engines is decreasing, and AI searches are constantly increasing, that’s a big issue for your business going forward.
That’s where LLMs.txt comes in. You may have heard the term come up in SEO circles a lot lately, and wondered exactly what it means. In short, it’s a simple file that acts like a map, helping artificial intelligence systems navigate and use your website’s content effectively.
Unlike the familiar robots.txt, which tells search engine bots what they can or cannot crawl, LLMs.txt is designed specifically for large language models (LLMs), the tech behind today’s AI chatbots and assistants. Let’s explore what LLMs.txt is, why it matters, and how you can use it to make your website AI-friendly.
What Is LLMs.txt?
LLMs.txt is a text file placed at the root of your website (like yourwebsite.com/llms.txt) that provides a clear, structured overview of your site’s content in a format AI systems can easily understand.
Think of it as a friendly guidebook for AI, pointing out your most important pages, summarising key information, and even offering full text in a clean, Markdown format. It’s not about controlling access like robots.txt; instead, it’s about delivering content in a way that AI can quickly process and use to answer user questions accurately.
For example, if you run a tech company with detailed product documentation, your LLMs.txt might include a summary of your software, links to key pages, or even the full text of your user guides. This helps AI systems like Perplexity or Google Gemini find and share your content when someone asks, “How does this software work?”
Why LLMs.txt Is Different from Robots.txt
If you’re familiar with SEO (search engine optimisation), you’ve likely heard of robots.txt and sitemap.xml. These files help search engines like Google crawl and index your site. But AI systems work differently—they don’t always crawl the web like Googlebot. Instead, they rely on direct access to content or specific prompts from users. Here’s how LLMs.txt stands out:
- Purpose: Robots.txt controls which parts of your site bots can access, using rules like “Disallow: /private/”. LLMs.txt doesn’t block or allow; it highlights your best content for AI to use, like a curated menu.
- Format: Robots.txt uses a simple text format with strict rules. LLMs.txt uses Markdown, a human- and machine-readable format with headings (#), lists (-), and links, making it easy for AI to parse.
- Use Case: Robots.txt is checked during web crawling for search indexing. LLMs.txt is used “on demand” when an AI needs to answer a question, like when someone asks about your brand or products.
- Content: Robots.txt is about access rules. LLMs.txt can include summaries, full text, or links to important pages, giving AI a quick snapshot of your site.
In short, robots.txt is like a gatekeeper, while LLMs.txt is a welcoming host, guiding AI to your most valuable content.
Why Should You Care About LLMs.txt?
As AI-powered search and chatbots become more popular, optimising for AI (sometimes called Generative Engine Optimisation or GEO) is just as important as traditional SEO. LLMs.txt helps your website stay visible in this new landscape. Here’s why it’s worth your attention:
- Better AI Visibility: AI systems often struggle with complex HTML, JavaScript, or cluttered web pages. LLMs.txt provides a clean, streamlined version of your content, increasing the chances that AI will cite or reference your site.
- Improved User Experience: When AI understands your content better, it can give more accurate, context-rich answers to users, which can drive more traffic to your site.
- Future-Proofing: AI search is growing fast. Early adopters of LLMs.txt can get a head start in making their sites AI-friendly, just like early SEO adopters benefited from optimising for Google.
- Control Over Content: By curating what AI sees, you can ensure it focuses on your most important pages or messages, rather than outdated or irrelevant content.
For example, Anthropic, the company behind Claude, has added an LLMs.txt file to its site, summarising its AI models and linking to key documentation. This makes it easier for other AI systems to reference Anthropic accurately.
How to Create an LLMs.txt File
Creating an LLMs.txt file is straightforward, especially if you’re already familiar with basic web files like sitemap.xml. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Decide What to Include
Think about what you want AI systems to know about your site. Common elements include:
- A brief summary of your website or business.
- Links to key pages (e.g., product pages, blog posts, or documentation).
- Full text of important content, like FAQs or user guides, in Markdown format.
- Optional metadata, like your site’s name or contact info.
For a small blog, your LLMs.txt might list your top posts. For a SaaS company, it might include API docs or pricing details.
2. Write in Markdown
Use Markdown for its simplicity and AI compatibility. Here’s a basic example:
# My Awesome Website
Welcome to My Awesome Website, your go-to source for tech tips and tutorials.
## About
We provide easy-to-follow guides on coding, AI, and web development.
## Key Pages
- [Home](https://mywebsite.com)
- [Learn Python](https://mywebsite.com/python)
- [AI Basics](https://mywebsite.com/ai-basics)
## Full Text: AI Basics
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming how we work and live. This guide covers the fundamentals of AI, including machine learning and LLMs...
This format is clean, structured, and easy for AI to read.
3. Save and Upload
Save the file as llms.txt and place it in your website’s root directory (yourwebsite.com/llms.txt). If you use WordPress, you can upload it to the public_html folder or use a plugin to manage it.
4. Test and Monitor
Check that the file is accessible by visiting yourwebsite.com/llms.txt in a browser. Use tools like Firecrawl or Mintlify to validate the format. Monitor your server logs to see if AI bots are accessing the file, and update it as your site changes.
Real-World Examples
Some companies are already embracing LLMs.txt:
- Mintlify, a documentation platform, added LLMs.txt support in November 2024, making thousands of developer docs AI-friendly overnight.
- Anthropic uses LLMs.txt to summarise its AI models and link to technical docs, boosting its visibility in AI responses.
- A personal website might use LLMs.txt to highlight a portfolio or blog, with a file size of 100 KB or more, containing full text for key pages.
These examples show how LLMs.txt can work for businesses, developers, or even individuals.
Challenges and Considerations
While LLMs.txt is promising, it’s still a proposed standard, not a universal rule. Here are some things to keep in mind:
- Adoption: Major AI providers like OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic haven’t fully committed to using LLMs.txt. For now, it’s more of a community-driven idea.
- No Enforcement: Unlike robots.txt, which bots are expected to follow, LLMs.txt is voluntary. AI systems might ignore it or not check for it at all.
- Maintenance: Like any web file, LLMs.txt needs regular updates to stay relevant as your site evolves.
- SEO Overlap: Some argue that existing tools like sitemap.xml and schema markup already help AI understand your site, making LLMs.txt less necessary.
Despite these challenges, LLMs.txt is easy to implement and low-risk, making it worth trying for sites that want to stay ahead in AI optimisation.
Tips for Maximising LLMs.txt Impact
To get the most out of LLMs.txt, follow these best practices:
- Keep It Simple: Focus on clear, concise content that AI can process quickly.
- Use Structured Data: Combine LLMs.txt with schema markup to give AI even more context about your pages.
- Avoid Conflicts: Ensure LLMs.txt doesn’t contradict your robots.txt rules (e.g., don’t link to pages blocked by robots.txt).
- Leverage Tools: Use generators like Firecrawl or community tools like llmstxt.directory to create and test your file.
- Monitor Traffic: Check if AI bots like ClaudeBot or PerplexityBot are accessing your LLMs.txt, and adjust based on their behavior.
The Future of LLMs.txt
As AI continues to shape how we find and share information, LLMs.txt could become as common as robots.txt or sitemap.xml. It’s part of a broader shift toward AI-driven search, where websites need to speak directly to algorithms, not just humans. If adopted widely, LLMs.txt could give website owners more control over how their content is used by AI, addressing concerns about data scraping and copyright.
For now, LLMs.txt is a low-effort, high-potential tool for making your site AI-ready. Whether you’re a blogger, a SaaS company, or a content creator, it’s a simple way to ensure AI systems can find and share your content accurately.
Get Started Today
Ready to make your website AI-friendly? Create an LLMs.txt file, upload it to your site, and start experimenting. It’s a small step that could give you a big advantage in the AI-powered search era. For more inspiration, check out examples on sites like Anthropic or explore tools like Mintlify and Firecrawl. Stay ahead of the curve, and let AI help your content shine!
Still need more help carrying this out, or curious about other ways to boost your web presence? Get in touch now!
How to Get Featured in AI Responses
As more and more people turn to AI tools like ChatGPT, Grok, or Claude to answer their questions, some sites are seeing a drop in organic traffic as fewer people click through to specific pages in search results. This shift means businesses need new ways to ensure their products or brands find the potential clients or customers they need.
One of the most important lucrative ways of doing this is to get your business or brand featured in AI responses.
Unlike traditional search engine optimisation (SEO), getting noticed by AI requires a fresh approach called Generative Engine Optimisation (GEO).
We’ve been running some tests on this for a while, and today we’re going to take you through clear, actionable steps to boost your visibility in AI responses, helping your brand or products stand out in this new era of search.
Why AI Responses Matter
AI-powered tools are rapidly changing how people find information. Instead of clicking through pages of search results, users now get quick, conversational answers from AI chatbots or tools like Google’s AI Overviews.
For example, if someone asks, “What’s the best running shoe for beginners?” an AI might summarise top recommendations and mention specific brands or products. If your brand isn’t included in these answers, you’re going to be missing out on customers and brand awareness.
Recent data shows that AI-driven search is growing fast. A 2025 survey found that 60% of UK adults have used a search page with an AI-generated summary, and the number of people using AI for online searches is expected to jump from 15 million in 2024 to 36 million by 2028. With no adverts currently available in most AI responses, getting your brand mentioned relies on smart strategies, not paid placements.
Let’s jump right into how you can make that happen.
1. Create High-Quality, Trustworthy Content

Perhaps the most generic answer since you should already be doing this if you want to get anywhere at all with your content - but it’s important enough that it simply can’t be skipped over. AI tools prioritise content that feels authentic, helpful, and credible. To get your brand or products featured, focus on creating content that AI trusts and wants to share.
Actionable Steps:
- Write clear, helpful content. Create blog posts, product descriptions, or guides that directly answer questions your customers might ask. For example, if you sell eco-friendly water bottles, write a post like “Why Stainless Steel Water Bottles Are Better for the Environment” with clear facts and benefits.
- Show expertise. Include insights from experts, customer reviews, or data to back up your claims. AI loves content that demonstrates authority. For instance, a study found that 61% of AI responses about brand reputation come from editorial media like trusted articles or reviews.
- Keep it fresh. Regularly update your website with new content to show it’s active and relevant. AI tools favour up-to-date information, so refresh product pages or blog posts with the latest details.
- Avoid fluff. Don’t stuff your content with repetitive keywords (like repeating “best water bottle” endlessly). Instead, use natural language that answers real questions, like “What makes a water bottle durable?”
Example:
If you run a small coffee shop, publish a blog post titled “How to Choose the Perfect Coffee Beans for Your Morning Brew.” Include tips, flavour profiles, and why your beans are unique. This kind of content is more likely to be picked up by AI when someone asks, “What are the best coffee beans?”
2. Use Structured Data to Help AI Understand Your Content

Structured data is like a roadmap that helps AI tools understand what’s on your website. It’s a simple way to tag your content so AI can quickly grasp details about your products or brand.
Actionable Steps:
- Add schema markup. Use tools like Google’s Schema Markup Generator to add tags to your website. For example, if you sell a gadget, tag it with “Product” schema to highlight its name, price, and reviews. This makes it easier for AI to pull your product into responses.
- Focus on key details. Include specifics like product features, prices, or availability in your structured data. For instance, if you sell running shoes, tag details like “water-resistant” or “best for marathon runners.”
- Test your markup. Use Google’s Rich Results Test to ensure your structured data is set up correctly. If it’s wrong, AI might skip your content.
Example:
For a bakery, add schema markup to your product pages for cakes, tagging details like “chocolate cake,” “serves 8,” and “gluten-free option.” When someone asks an AI, “Where can I find gluten-free cakes nearby?” your bakery has a better chance of being mentioned.
3. Get Mentioned on Trusted Websites

AI tools often pull information from well-known, authoritative websites like news outlets, industry blogs, or review sites. Getting your brand or products mentioned on these platforms can significantly boost your chances of appearing in AI responses.
Actionable Steps:
- Reach out to industry publications. Contact blogs, magazines, or websites in your niche to feature your product. For example, if you sell fitness gear, pitch a story to a fitness blog about how your dumbbells are perfect for home workouts.
- Collaborate with influencers. Work with influencers or reviewers who can talk about your product on their platforms. Their mentions can signal to AI that your brand is trustworthy.
- Get listed in directories. Submit your business to reputable directories like Yelp or industry-specific lists. These mentions add credibility and increase your visibility.
- Monitor your mentions. Use tools like Google Alerts to track where your brand is mentioned online and ensure the information is accurate.
Example:
If you sell skincare products, send samples to a beauty blogger for a review. If their review gets picked up by an AI tool answering “What’s the best moisturiser for dry skin?” your product could be featured.
4. Optimise for Conversational Questions

AI tools are designed to answer questions the way people talk, like “What’s the best laptop for students?” or “Where can I buy sustainable clothing?” To get your brand into these responses, create content that matches these conversational queries.
Actionable Steps:
- Research common questions. Use tools like AnswerThePublic or Google’s “People Also Ask” to find questions your audience is asking. For example, a pet store might find questions like “What’s the healthiest dog food for puppies?”
- Write conversational content. Create FAQ pages or blog posts that directly answer these questions. Use natural phrases like “If you’re looking for a budget-friendly laptop, here’s why our model stands out.”
- Use strategic text sequences. Include natural, relevant phrases in your content that match how people ask questions. For example, instead of just “dog food,” write “our organic dog food is great for sensitive stomachs.” Avoid overstuffing keywords, as AI can detect unnatural language.
- Test your visibility. Search for your products on AI tools like ChatGPT or Perplexity to see if they appear. If not, tweak your content to better match the questions AI is answering.
Example:
A travel agency could create a page answering “What are the best family-friendly holiday spots in 2025?” with detailed recommendations and mentions of their packages. This increases the chance of AI citing their services.
5. Make Your Website Fast and Mobile-Friendly

AI tools favour websites that load quickly and work well on phones. If your site is slow or hard to use on a smartphone, AI might skip it when pulling information.
Actionable Steps:
- Check your site speed. Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights to see how fast your website loads. Aim for a score above 90 on mobile and desktop.
- Optimise for mobile. Ensure your website is easy to navigate on phones. Test it on different devices to confirm buttons, images, and text display correctly.
- Fix technical issues. Use tools like Screaming Frog to find broken links or missing metadata that could hurt your site’s performance.
- Keep it simple. Avoid heavy images or complex designs that slow down your site. Compress images using tools like TinyPNG.
Example:
If you sell handmade jewellery, ensure your online store loads quickly and looks great on mobile. A slow site might mean AI overlooks your products when answering “Where can I buy unique necklaces?”
6. Build a Strong Brand Reputation

AI tools prioritise brands that seem trustworthy and well-regarded. A strong online reputation can make your brand more likely to be mentioned in AI responses.
Actionable Steps:
- Encourage customer reviews. Ask happy customers to leave reviews on Google, Yelp, or your website. Positive reviews signal credibility to AI.
- Manage negative feedback. Respond professionally to negative reviews to show you care about customers. AI may pick up on this as a sign of trustworthiness.
- Engage on social media. Share valuable content on platforms like Instagram or LinkedIn to build your brand’s authority. AI tools often consider social media presence when evaluating credibility.
- Audit your AI visibility. Use services like Alexander PR’s 360° LLM Reputation Audit to see how your brand appears across AI platforms like ChatGPT or Gemini. This can help you spot and fix gaps.
Example:
A local restaurant could encourage diners to leave Google reviews about their signature dish. If someone asks an AI, “What’s the best Italian restaurant in town?” positive reviews could help the restaurant get mentioned.
7. Leverage Multimedia Content

AI tools are starting to pull information from images, videos, and other media, especially with features like Google’s Circle to Search. Adding multimedia to your strategy can boost your chances of being noticed.
Actionable Steps:
- Create engaging videos. Make short videos showcasing your products, like a tutorial on how to use your kitchen gadget. Post them on YouTube or your website.
- Optimise images. Add descriptive alt text to images on your site, like “handmade leather wallet in brown” for a wallet photo. This helps AI understand your visuals.
- Use infographics. Create simple infographics that summarise key information, like “5 Benefits of Our Organic Dog Treats.” AI may pull these into responses.
- Tag multimedia with schema. Use structured data for videos or images to make them easier for AI to find.
Example:
A fitness brand could post a YouTube video titled “10-Minute Home Workout with Our Resistance Bands.” With proper tags and descriptions, this video could appear in AI answers to “What’s a quick home workout?”
8. Stay Ahead with Regular Monitoring

AI search is always evolving, so you need to keep track of how your brand is performing and adjust your strategy as needed.
Actionable Steps:
- Track AI mentions. Regularly check AI tools like ChatGPT or Perplexity to see if your brand or products appear in relevant queries. Note what’s working and what isn’t.
- Use analytics tools. Tools like HubSpot’s AI Search Grader can show how your brand performs in AI search and suggest improvements.
- Stay updated on AI trends. Follow industry blogs or newsletters to learn about new AI search features or updates.
- Test and tweak. Experiment with different content styles or keywords and see how they affect your AI visibility. For example, try rephrasing product descriptions to match common AI queries.
Example:
A tech startup selling smart home devices could check if their products appear in AI answers to “What’s the best smart thermostat?” If not, they could update their website with a blog post answering that exact question.
9. Incorporate Statistics and Data-Driven Insights

AI systems often prioritise content backed by credible data, as it signals authority and reliability. Including statistics or research findings in your content can make it more likely to be cited by AI tools.
Actionable Steps:
- Use credible sources. Reference studies, surveys, or industry reports in your content. For example, cite a 2025 report showing “75% of consumers prefer eco-friendly products” to support your sustainable brand.
- Create original data. Conduct small surveys or studies related to your niche and publish the findings. For instance, a pet brand could survey customers on “Top 5 Pet Food Preferences in 2025.”
- Visualise data. Use charts or infographics to present statistics clearly, making it easier for AI to parse and cite.
Example:
A sustainable clothing brand could publish a blog post titled “Why 80% of UK Shoppers Choose Sustainable Fashion in 2025,” referencing a recent industry study. This could be picked up by AI for queries like “What’s the best sustainable clothing brand?”
10. Optimise for Local Search

If your business serves a specific region, optimising for local AI search is crucial, as AI tools often provide location-specific answers.
Actionable Steps:
- Claim your Google Business Profile. Ensure your profile is complete with accurate details like address, hours, and services. This helps AI recommend your business for local queries.
- Use local keywords. Include location-specific phrases in your content, like “best coffee shop in Manchester” or “London eco-friendly products.”
- Encourage local reviews. Ask customers to mention your location in reviews, as AI tools often rely on this for local recommendations.
Example:
A Manchester-based florist could optimise their site with phrases like “fresh flowers in Manchester” and claim their Google Business Profile. When someone asks, “Where can I buy flowers in Manchester?” AI is more likely to mention them.
11. Focus on User Intent and Semantic Search

AI tools are adept at understanding user intent and context. To align with this, your content must address the “why” behind user queries, not just the “what.”
Actionable Steps:
- Analyse intent. Identify whether users are seeking information, solutions, or purchases. For example, “best laptop for students” implies a buying intent, so highlight product benefits and purchase options.
- Use LSI keywords. Incorporate related terms like “durable laptop,” “student-friendly tech,” or “budget laptops” to align with semantic search.
- Answer the full query. Create content that fully addresses the user’s question, including related subtopics. For example, a post on “best laptops” could also cover battery life, portability, and price ranges.
Example:
A tech retailer could write a blog post titled “Best Laptops for UK Students in 2025: Budget, Performance, and Portability,” addressing multiple aspects of the query to increase AI pickup.
Putting It All Together
Getting your products or brand into AI responses isn’t about gaming the system—it’s about being helpful, trustworthy, and easy for AI to find. By creating high-quality content, using structured data, building a strong reputation, leveraging multimedia, incorporating data, optimising for local and semantic search, and staying adaptable, you can increase your chances of being featured in AI answers. Start with one or two steps, like adding schema markup or writing a conversational blog post, and build from there.
As AI search continues to grow, businesses that act now will have a head start. Don’t let your brand get lost in the shift away from traditional search engines. Follow these steps, monitor your progress, and watch your visibility soar in the AI-driven world.